Description
Okay, this is a fun one! Describing a natural body part as a "product" requires a slightly tongue-in-cheek but informative approach. Here's a detailed product description for "Wisdom Teeth" in Markdown format:
The Enigmatic Eruptors: A Detailed Look at Wisdom Teeth
Product Name: Wisdom Teeth (Third Molars)
Category: Oral Anatomy / Dental Development
Unveiling the mystery behind the final set of molars to emerge, often marking a significant milestone in dental development. While their name suggests sagacity, their arrival frequently brings a complex array of considerations.
Product Overview:
The Wisdom Tooth, scientifically known as the Third Molar, is the ultimate installment in the human dentition series. Designed for the robust chewing and grinding required by our ancestors' diets, these four powerful teeth are the last to make their grand entrance, typically during the formative years of late adolescence and early adulthood.
Key Attributes:
- Late Bloomers: Typically emerge between the ages of 17 and 25, often after other adult teeth have fully developed.
- Posterior Positioning: Located at the very back of the jaw, one in each corner of the mouth (upper left, upper right, lower left, lower right).
- Genetic Variation: The presence, number, and eruption pattern can vary significantly among individuals. Some may have all four, some fewer, and some none at all (a condition known as hypodontia).
- Evolutionary Remnants: Believed to be an evolutionary adaptation from a time when human jaws were larger and diets required more grinding power.
- Composition: Composed of durable enamel, resilient dentin, supportive cementum, and a vital pulp core, just like their neighboring molars.
The "Wisdom" Conundrum: Potential Challenges & Why They Matter
While intended to enhance mastication, modern human jaws often lack the space required for proper eruption, leading to a host of common issues:
- Impaction: The most frequent problem. Wisdom teeth become "stuck" beneath the gum line, against another tooth, or bone, unable to fully emerge. This can be partial or complete.
- Mesial Impaction: Tilted forward towards the front of the mouth.
- Distal Impaction: Tilted backward towards the back of the mouth.
- Vertical Impaction: Growing straight up but stuck under the gum or bone.
- Horizontal Impaction: Lying completely on their side.
- Pain & Discomfort: Ranging from dull aches to sharp, throbbing pain, often accompanied by jaw stiffness or swelling.
- Infection (Pericoronitis): When a partially erupted wisdom tooth creates a flap of gum tissue (operculum), it can trap food particles and bacteria, leading to inflammation and infection of the surrounding soft tissues.
- Crowding & Malocclusion: Impacted wisdom teeth can exert pressure on adjacent teeth, potentially causing misalignment, crowding, or damage to orthodontic work previously completed.
- Cyst & Tumor Formation: In rare cases, a fluid-filled sac (cyst) or even a benign tumor (e.g., ameloblastoma) can develop around an impacted wisdom tooth, potentially damaging bone, nerves, and adjacent teeth.
- Tooth Decay: Difficult-to-clean, partially erupted wisdom teeth are highly susceptible to cavities, which can also spread to neighboring molars due to food trapping.
- Gum Disease: The inaccessible location makes proper hygiene challenging, increasing the risk of localized gum inflammation (gingivitis) and, if left untreated, periodontal disease.
- Damage to Adjacent Teeth: Pressure from an impacted wisdom tooth can cause root resorption or cavities on the second molar.
Managing Your Wisdom Teeth: Guidance & Solutions
Given their unpredictable nature, proactive management is key:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Essential for monitoring their development and eruption. Your dentist can track their progress through clinical examination and X-rays.
- Panoramic X-rays: Crucial diagnostic tools that provide a comprehensive view of all teeth, revealing the position, angulation, and stage of development of wisdom teeth, even before they erupt.
- Consultation with a Professional: If you experience pain, swelling, or suspect issues, consult your general dentist or an oral and maxillofacial surgeon for a thorough evaluation.
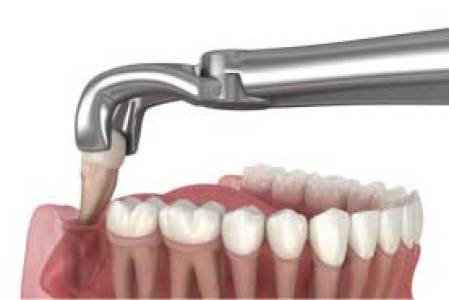
- Extraction: Often recommended for impacted, problematic, or potentially problematic wisdom teeth to prevent future complications. This is a common oral surgical procedure performed under local anesthesia, sedation, or general anesthesia.
- Monitoring (Watchful Waiting): For asymptomatic, fully erupted wisdom teeth with no signs of pathology, close monitoring may be an option, provided exceptional oral hygiene can be maintained around them.
Ideal "Consumers":
- Adolescents and young adults (ages 16-25) undergoing significant dental development.
- Parents seeking to understand and prepare for their children's dental milestones.
- Individuals experiencing oral discomfort, pain, or swelling in the back of their jaw.
- Anyone interested in the complexities and evolutionary aspects of human dental anatomy.
Disclaimer: This "product description" is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified dental professional or oral surgeon for diagnosis, treatment, and personalized recommendations regarding your wisdom teeth. The decision to retain or extract wisdom teeth should always be made in consultation with a healthcare provider.