Description
Pulp Therapy: Preserving Primary Teeth for Healthy Smiles
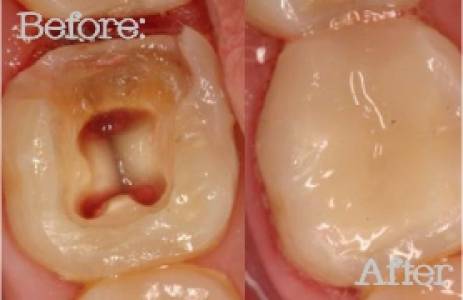
In pediatric dentistry, preserving the natural dentition is paramount for a child's overall oral health and development. When deep caries or trauma threaten the vitality of primary (baby) teeth, Pulp Therapy offers a critical and highly effective intervention designed to save these teeth until their natural exfoliation.
What is Pulp Therapy?
Pulp Therapy refers to a range of endodontic treatments specifically adapted for primary teeth. Its primary goal is to maintain the integrity and vitality of a compromised tooth by treating inflamed or infected pulp tissue, thereby preventing premature extraction and allowing the tooth to remain functional until its natural replacement by a permanent successor. It's often likened to a "root canal for baby teeth," though the procedures are distinct and less complex due to the unique anatomy of primary teeth.
Key Features & Benefits
- Tooth Preservation: The ultimate goal is to save the natural tooth structure, preventing the complications associated with premature tooth loss.
- Avoids Premature Extraction: Eliminates the need for early tooth removal, which can be traumatic for children and lead to more complex issues.
- Maintains Arch Space: Preserving primary teeth ensures proper space for the eruption of permanent teeth, preventing crowding and potential malocclusion in the future.
- Restores Function and Comfort: Alleviates pain and discomfort, allowing children to chew, speak, and maintain normal oral functions without hindrance.
- Promotes Aesthetic and Psychological Well-being: Maintains a full, healthy smile, which is important for a child's self-esteem and confidence.
- Encourages Healthy Oral Development: Supports the development of proper chewing patterns and aids in the natural progression of permanent tooth eruption.
- Versatile Treatment Modalities: Encompasses various techniques tailored to the extent of pulp involvement:
- Pulpotomy: Partial removal of inflamed coronal pulp tissue, with the remaining radicular pulp preserved.
- Pulpectomy: Complete removal of all infected coronal and radicular pulp tissue, followed by obturation with a resorbable filling material.
- Utilizes Advanced Biocompatible Materials: Employs materials like Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA), Calcium Hydroxide, or zinc oxide-eugenol (ZOE) cements known for their efficacy and safety in pediatric applications.
- Often Followed by Full Coverage Restoration: Typically, a stainless steel crown (SSC) is placed post-pulp therapy to protect the treated tooth from fracture and ensure long-term success.
Indications for Pulp Therapy
Pulp therapy is indicated for primary teeth exhibiting:
- Deep Carious Lesions: Cavities that extend near or into the pulp chamber, causing reversible or irreversible pulpitis.
- Traumatic Injuries: Fractures or luxations that expose the pulp or compromise its vitality.
- Spontaneous Pain: Pain that occurs without an obvious stimulus, often indicative of irreversible pulpitis.
- Prolonged Sensitivity: Persistent pain to thermal changes or sweets after the stimulus is removed.
- No Pathological Root Resorption: Absence of internal or external root resorption affecting the permanent successor.
- Restorable Tooth Structure: Sufficient remaining tooth structure to allow for a successful restorative outcome, typically with a stainless steel crown.
Contraindications for Pulp Therapy
Pulp therapy is generally not recommended for primary teeth with:
- Extensive Tooth Structure Loss: Where the tooth is non-restorable due to severe destruction.
- Pathological Internal or External Root Resorption: Indicating widespread and irreversible damage to the root structure.
- Uncontrolled Swelling, Abscess, or Fistula: Signs of chronic infection or necrosis that cannot be resolved by pulp therapy alone.
- Radiographic Evidence of Furcation or Periapical Pathology: Suggests advanced infection beyond the pulp chamber.
- Physiological Root Resorption Exceeding Two-thirds: When the tooth is naturally nearing exfoliation.
- Uncontrolled Systemic Diseases: In patients who are immunocompromised or have conditions that make them poor candidates for dental procedures requiring infection control.
The Pulp Therapy Procedure (Simplified Overview)
- Diagnosis: Thorough clinical and radiographic examination to assess pulp status and determine the appropriate therapy.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthetic administration to ensure the child's comfort.
- Isolation: Use of a rubber dam to isolate the tooth, maintaining a sterile field and protecting the child from materials.
- Caries Removal: All carious dentin is carefully removed.
- Pulp Access: The pulp chamber is carefully accessed.
- Pulp Treatment:
- Pulpotomy: Coronal pulp is removed, hemostasis is achieved, and a medicament (e.g., MTA, calcium hydroxide) is placed over the radicular pulp stumps.
- Pulpectomy: Entire coronal and radicular pulp is removed, canals are cleaned and shaped, and then filled with a resorbable material (e.g., ZOE paste).
- Final Restoration: The tooth is typically restored with a full-coverage crown, most commonly a stainless steel crown, to protect it from fracture and ensure long-term success.
Why Choose Pulp Therapy?
Pulp Therapy is a cornerstone of comprehensive pediatric dental care. By opting for this treatment, dental professionals empower children to maintain their natural dentition, support proper oral function, and prevent more complex and costly orthodontic or restorative issues in the future. It reflects a commitment to a child-centric approach, prioritizing comfort, health, and the foundation for a lifetime of healthy smiles.
Target Audience
- Pediatric Dentists
- General Dentists providing pediatric care
- Dental educators and students
Disclaimer: This description provides general information about Pulp Therapy. Specific treatment plans must be determined by a qualified dental professional based on a thorough examination and diagnosis of the individual patient's condition.